Tips for Training Your New Puppy

Bringing a new puppy home inevitably means tackling training across essential areas like housebreaking, basic obedience, manners, socialization, and more. While puppies charm with their cute antics, failing to establish good habits early burdens behaviors later when accidental damage, jumping on guests, or reactive barking socially challenges adult dogs. So, new owners need proper techniques to facilitate important lifelong training.
Core focus areas involve potty skills, minimizing nipping, basic commands, proper play, and crate acclimation. Building the right foundation early through positive reinforcement, patience, and consistency sets up owners and dogs for harmonious cohabitation. This article outlines top training tips to ensure new puppies blossom into well-adapted adult companions.
Establish a Schedule
Maintaining a consistent daily schedule aligned to predictable patterns aids puppies in learning and meeting expectations faster. Puppies thrive on regular cycles of eating, playing, training, exercising, and sleeping, just like infants. Feeding meals and taking potty breaks at consistent times every day syncs their biological digestion process, allowing puppies to start predicting appropriate windows for relieving themselves. This proves essential for accelerating house training. Waking up, mealtimes, and lights out also benefit from fixed schedules.
Reliable routines teaching puppies when to expect walks, play sessions, or training repetition capitalizes on their acute perception honed evolutionarily for decoding human behavior patterns. Adhering to scheduled cycles and avoiding randomness minimizes accidents while fast-tracking learning when specific needs get fulfilled.
Crate Train Gradually
Proper crate training starts early and positively acclimates confinement while preventing unwanted behavioral issues or destructive tendencies when left unsupervised later on. First, introduce the open crate during awake times, allowing curious puppy exploration with treats placed inside to incentivize voluntary entrance. As your puppy appears comfortable resting inside with the door open, practice briefly closing the door while right nearby praising calmness and giving treats through holes/bars. Release immediately if there are signs of distress. Slowly build the duration of closed crate relaxation sessions through positive reinforcement.
Only progress increments when your puppy feels fully at ease while confined based on body language cues. Rushing steps or forcing duration risks traumatic associations. Once achieving several hours of tranquility in the closed crate without accidents, test short solo sessions errands before hitting full workday stretches. Proper gradual acclimation sets up lifelong confinement composure when necessary.
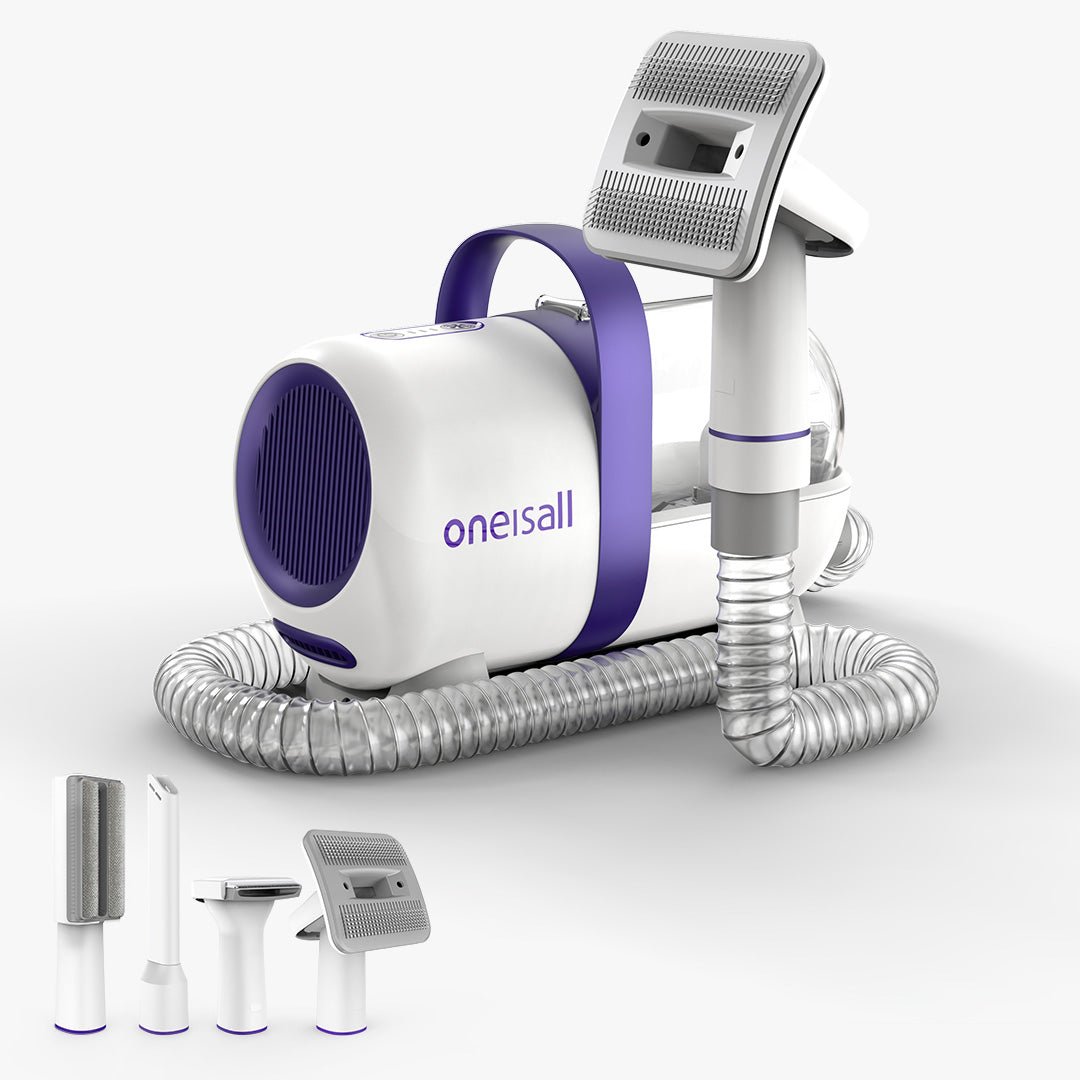
Pet grooming
Pet grooming refers to the hygienic care and cleaning of a pet's hair, skin, nails, teeth, and ears. It includes brushing, bathing, trimming hair, clipping nails, cleaning ears, and checking for signs of infection or other health problems.
Regular pet grooming is an important part of pet care and maintenance. It helps keep pets clean and free of dirt, tangled hair, parasites, and skin irritations or infections. Grooming also provides an opportunity to monitor a pet's health by looking for lumps, sore spots, or signs of illness.
Reward Desired Behaviors
Catching and rewarding desirable puppy behaviors using high-value treats and affection establishes positive habits that meet household etiquette standards. Consistently treating calm interactions with humans and other pets coupled with obedience cues like sit teaches puppies these represent beneficial behaviors deserving repetition. Maintain vigilance for accident-free potty signals or play unescalating into roughness so prompt praise incentivizes the good decision while interrupting unwanted acts and avoids inadvertent reinforcing through delayed attention.
Noticing and praising wanted behaviors, especially subtle intricacies like making eye contact when their name is called or maintaining a loose leash stride focus, trains dogs what earns coveted rewards, building lifelong conduct. Equally important - address problematic behaviors compassionately, not punitively, as punishing fearful, confused, or rambunctious pups intensifies anxiety and resistance.
Use a Command for Potty Time
Assigning a distinct potty cue word expedites the concept of acceptable bathroom needs relief locations versus accidents inside. Every time you bring your pup outside to their designated potty area, use a specific phrase like "Go Potty" and clip it to their relieving moment with praise. Over time, repeating this ritual connects the command as a signal for the desired elimination, while affirmations confirm appropriate performance. Soon, puppies associate hearing their potty command with both where and when to eliminate on cue as opposed to struggling with generalized house accidents that lack context. Just like "Sit" means hindquarters go down, assigning "Go Potty" indicates precise occasions and locations for urinating or defecting as wanted.
Manage Accidents Compassionately
When indoor accidents occur before fully housebroken, compassionately clean messes while limiting subsequent access to problem rooms through managed containment or supervision; remember, puppies lacking complete bladder and bowel control get confused without adequate external direction regarding proper potty etiquette. Risk frustration cleaned carpets unless enzymatic cleansers completely neutralize odors, avoiding repeat occurrences where previous scents prompt recapitulation.
Rather than scolding unpreventable mistakes or expecting too much too soon before muscle maturity, set your pup up for success, restricting the free reign of your home initially. Allow them to earn house freedom gradually as accident frequency declines with positive reinforcement training. Protect your floors while establishing the habits gradually through understanding and guidance.
Discourage Nipping Early
Since puppy nibbling often starts innocently without inherent aggression, address inappropriate nibbling promptly before escalating into dangerous adult biting behavior. Redirect attempts using proper chew toys instead while saying "No bite!" then ignore them if excessive mouthing persists to discourage attention rewards. Provide towel knots frozen with chicken broth to sore teething gums, but limit access if chewing turns obsessive. Also, teach appropriate play bite force inhibition through high-pitched Yelping when jaws clamp too hard. Playing only gently without biting while praising gentle mouths reinforces rules for acceptable human contact. Intervene at first signs of skin contact beyond licking before roughhousing intensifies or kids get injured, eliciting defensive aggression.
Practice Loose Leash Walking
Avoid pulling early on by working in tempting but controlled environments with reward treats and by stopping movement when leashes tighten. Gradually challenge hyperactivity, extending session duration and curbing sniff detours. Narrow sidewalks between fences streamline focus. Reward slack leash strides with treats and collar grabs, releasing upon tight pulls briefly. Let the pup learn to achieve the forward progress they desire by choosing loose leash continuity with you. Pulling ahead risks getting "stuck" with nowhere to go, like trucks air braking at green lights with impatient tailgaters. Loose Leash manners mastered early form lifetime habits bypassing heavy puller behavior.
Practice Basic Cues Using Treat Lures
They are luring puppies into basic obedience positions using treats held above eye level just beyond their nose primes reflexive, responsive behaviors, preparing for hand signal and verbal conditioned cue phases. Present treats directing their nose down and back slowly until their bottom touches, signaling the "Sit" position.
Mark and reward compliance once seated. Repeat gently guiding down to elbows lifted off the ground, luring puppies into "Down” positions. Treat upon lying down, then add the verbal Down cue and hand signals. The same luring approach works for "Wait," "Come," "Up" onto hind legs, "Off" furniture, and more priming action understanding before solidifying compliance to just commands. Keep early sessions positive and under 5 minutes to avoid mental exhaustion building up duration gradually. Soon, they respond reliably to just verbal and visual cues, earning treats.
Guide Appropriate Play Styles
Discourage early puppy play roughness through distraction before escalation risks as they age and gain strength. Redirect mouthing onto chew rope tugs and teach them an acceptable level of bite force inhibition when interacting with humans or fellow pets. Say "Gentle" in calm but firm tones when incisors clamp down too hard during play, and then praise at lessened intensities. Encourage gentle play wrestling and tug interactions praising reciprocal manners. Promptly interrupt obsessive toy guarding, aggressive mounting, or fight inciting through distraction and separation. Helping young puppies express themselves through positive and safe social engagements prevents behavioral issues arising from excessive physical or social repression. Establishing rules for appropriate play early is easier than attempting to correct intense adult play habits already rehearsed.
Socialize Continually
Once vaccines fully protect puppy immunity, immediately enroll them in structured socialization class environments, ensuring extensive positive exposures to novel dogs, people, places, and circumstances. Safely exercising sociability helps prevent wariness or reactivity towards unfamiliar stimuli from under-exposure during prime developmental months. Maintain safe socialization throughout adulthood, introducing new places, smells, sounds, animals, and people to maintain confidence. Stay vigilant for overstimulation signals like lip licking or yawning, prompting anxiety or exhaustion. Help timid puppies warm up gently at their pace rather than flooding with too much too quickly. Risk under socialization manifests later as aggression or overstimulation, fueling chronic anxiety. Proper socialization through compassion builds worldly canine citizens.
Conclusion
Training puppies appropriately relies on compassion, patience, and persistence through positive reinforcement, scheduling consistency, and socialization support. Guarantee your new puppy blossoms into a happy household companion by establishing optimal habits early. Keep sessions brief, creative, and fun, avoiding anger, anxiety, or punishment permeability dynamics compromising trust and rapport. Your devoted leadership now pays lifelong dividends, ensuring harmonious cohabitation and minimizing stressful behaviors. Maintain realistic expectations for puppy development stages while proactively addressing challenges like proper bathroom needs communication, loose leash manners, safe play styles, and basic obedience. With caring guidance fostering essential skills suited for their environment, new puppies flourish with their loved ones.